The nitrogen cycle is one of the essential biogeochemical cycles that involves the transformation of nitrogen into different forms, making it usable for plants and animals. Nitrogen (N₂) is a crucial component of amino acids, proteins, and DNA. Although nitrogen is abundant in the atmosphere (about 78%), most organisms cannot directly utilize atmospheric nitrogen. The nitrogen cycle converts this inert nitrogen into a usable form.
नाइट्रोजन चक्र एक महत्वपूर्ण जैव-भू रासायनिक चक्र है, जो नाइट्रोजन को विभिन्न रूपों में बदलकर पौधों और जानवरों के लिए उपयोगी बनाता है। नाइट्रोजन (N₂) अमीनो एसिड, प्रोटीन और डीएनए का एक प्रमुख घटक है। यद्यपि वायुमंडल में नाइट्रोजन प्रचुर मात्रा में होती है (लगभग 78%), अधिकांश जीव सीधे वायुमंडलीय नाइट्रोजन का उपयोग नहीं कर सकते हैं। नाइट्रोजन चक्र इस निष्क्रिय नाइट्रोजन को उपयोगी रूप में परिवर्तित करता है।
Steps of the Nitrogen Cycle | नाइट्रोजन चक्र के चरण
The nitrogen cycle consists of several critical stages. These stages help convert nitrogen into a form that organisms can use.
नाइट्रोजन चक्र के कई महत्वपूर्ण चरण होते हैं। ये चरण नाइट्रोजन को एक ऐसे रूप में बदलने में मदद करते हैं जिसे जीव उपयोग कर सकें।
1. Nitrogen Fixation | नाइट्रोजन स्थिरीकरण
Nitrogen fixation is the first step, where atmospheric nitrogen (N₂) is converted into ammonia (NH₃) by bacteria, particularly Rhizobium, found in the root nodules of legumes, or through industrial processes.
नाइट्रोजन स्थिरीकरण पहला चरण है, जहाँ वायुमंडलीय नाइट्रोजन (N₂) को अमोनिया (NH₃) में परिवर्तित किया जाता है। यह प्रक्रिया जीवाणुओं, विशेष रूप से राइजोबियम द्वारा किया जाता है, जो फलियों की जड़ों में पाया जाता है, या औद्योगिक प्रक्रियाओं के माध्यम से होता है।
2. Nitrification | नाइट्रीकरण
In nitrification, ammonia (NH₃) is converted into nitrites (NO₂⁻) and then into nitrates (NO₃⁻) by nitrifying bacteria such as Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter. Plants can absorb these nitrates for their growth.
नाइट्रीकरण में, अमोनिया (NH₃) को नाइट्राइट्स (NO₂⁻) और फिर नाइट्रेट्स (NO₃⁻) में बदल दिया जाता है, जो नाइट्रोसोमोनस और नाइट्रोबैक्टर जैसे नाइट्रीकरण जीवाणुओं द्वारा किया जाता है। पौधे इन नाइट्रेट्स को अपने विकास के लिए अवशोषित कर सकते हैं।
3. Assimilation | समावेशन
During assimilation, plants absorb nitrates (NO₃⁻) from the soil through their roots. These nitrates are used to form plant proteins and other essential compounds.
समावेशन के दौरान, पौधे मिट्टी से नाइट्रेट्स (NO₃⁻) को अपनी जड़ों के माध्यम से अवशोषित करते हैं। इन नाइट्रेट्स का उपयोग पौधों के प्रोटीन और अन्य आवश्यक यौगिकों के निर्माण में किया जाता है।
4. Ammonification | अमोनिफिकेशन
When plants and animals die or excrete waste, the nitrogen in their bodies is converted back into ammonia (NH₃) by decomposing bacteria in a process called ammonification.
जब पौधे और जानवर मर जाते हैं या अपशिष्ट उत्सर्जित करते हैं, तो उनके शरीर में मौजूद नाइट्रोजन को विघटित करने वाले जीवाणु अमोनिफिकेशन प्रक्रिया के माध्यम से फिर से अमोनिया (NH₃) में बदल देते हैं।
5. Denitrification | अपघटन
The final stage, denitrification, is where nitrates (NO₃⁻) are converted back into atmospheric nitrogen (N₂) by denitrifying bacteria, such as Pseudomonas, releasing nitrogen back into the atmosphere.
अंतिम चरण, अपघटन, वह प्रक्रिया है जिसमें नाइट्रेट्स (NO₃⁻) को डिनाइट्रीफाइंग जीवाणुओं, जैसे प्स्यूडोमोनस, द्वारा वापस वायुमंडलीय नाइट्रोजन (N₂) में परिवर्तित किया जाता है, जिससे नाइट्रोजन फिर से वायुमंडल में वापस लौटती है।
Diagram of Nitrogen Cycle | नाइट्रोजन चक्र का चित्र
Here is a simplified diagram of the nitrogen cycle, showcasing all the key stages:
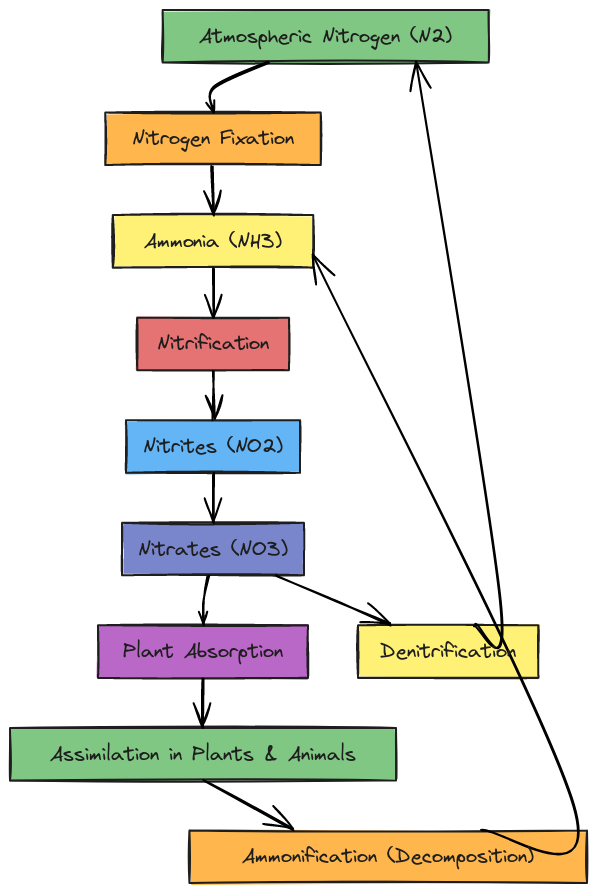
इस नाइट्रोजन चक्र के चित्र में सभी प्रमुख चरणों को दर्शाया गया है:
Importance of Nitrogen Cycle | नाइट्रोजन चक्र का महत्व
The nitrogen cycle is vital for maintaining the balance of ecosystems. It ensures that nitrogen is converted into forms that are usable by plants, which in turn supports the food chain. Without this cycle, life on Earth would be unsustainable.
नाइट्रोजन चक्र पारिस्थितिक तंत्र के संतुलन को बनाए रखने के लिए अत्यधिक महत्वपूर्ण है। यह सुनिश्चित करता है कि नाइट्रोजन उन रूपों में परिवर्तित हो जाए जिसे पौधे उपयोग कर सकें, जिससे खाद्य श्रृंखला को समर्थन मिले। इस चक्र के बिना, पृथ्वी पर जीवन असंभव हो जाएगा।
Nitrogen Fixation and Nitrification | नाइट्रोजन स्थिरीकरण और नाइट्रीकरण
Nitrogen Fixation
As explained earlier, nitrogen fixation is the process where nitrogen is made available to plants by converting atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia. This is a key process in the nitrogen cycle.
जैसा कि पहले बताया गया है, नाइट्रोजन स्थिरीकरण वह प्रक्रिया है जिसमें वायुमंडलीय नाइट्रोजन को अमोनिया में बदलकर पौधों के लिए उपलब्ध कराया जाता है। यह नाइट्रोजन चक्र की एक प्रमुख प्रक्रिया है।
Nitrification
Nitrification is another important step where ammonia is further converted into nitrites and nitrates by specific bacteria. These nitrates are then absorbed by plants, completing a crucial part of the nitrogen cycle.
नाइट्रीकरण एक और महत्वपूर्ण चरण है, जिसमें अमोनिया को विशेष जीवाणुओं द्वारा नाइट्राइट्स और नाइट्रेट्स में परिवर्तित किया जाता है। ये नाइट्रेट्स फिर पौधों द्वारा अवशोषित किए जाते हैं, जो नाइट्रोजन चक्र का एक महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा पूरा करते हैं।
Biological and Industrial Nitrogen Fixation | जैविक और औद्योगिक नाइट्रोजन स्थिरीकरण
Biological nitrogen fixation occurs naturally in the environment, mainly through nitrogen-fixing bacteria. These bacteria live in symbiotic relationships with plants, particularly legumes. This natural process supports the nitrogen needs of ecosystems.
औद्योगिक नाइट्रोजन स्थिरीकरण, जैसे कि हैबर-बॉश प्रक्रिया, मानव निर्मित नाइट्रोजन उर्वरकों के उत्पादन के लिए उपयोग किया जाता है, जो कृषि में व्यापक रूप से इस्तेमाल होता है।
जैविक नाइट्रोजन स्थिरीकरण प्राकृतिक रूप से वातावरण में होता है, मुख्य रूप से नाइट्रोजन स्थिरीकरण करने वाले जीवाणुओं के माध्यम से। ये जीवाणु पौधों के साथ सहजीवी संबंधों में रहते हैं, विशेष रूप से फलियों के साथ। यह प्राकृतिक प्रक्रिया पारिस्थितिक तंत्र की नाइट्रोजन आवश्यकताओं को पूरा करती है।
Industrial nitrogen fixation, such as the Haber-Bosch process, is used for producing nitrogen-based fertilizers widely used in agriculture.
Role of Nitrogen in the Environment | पर्यावरण में नाइट्रोजन की भूमिका
Nitrogen is a fundamental element that plays a vital role in:
- Plant growth: Nitrogen is a component of chlorophyll, which plants use in photosynthesis.
- Protein synthesis: It is a key element in amino acids and proteins, essential for the growth of all living organisms.
- Ecosystem balance: The nitrogen cycle maintains a balance between nitrogen in the atmosphere, soil, and living organisms.
नाइट्रोजन एक मूलभूत तत्व है जो निम्नलिखित में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है:
- पौधों की वृद्धि: नाइट्रोजन क्लोरोफिल का घटक है, जिसका उपयोग पौधे प्रकाश संश्लेषण में करते हैं।
- प्रोटीन संश्लेषण: यह अमीनो एसिड और प्रोटीन का एक प्रमुख तत्व है, जो सभी जीवों की वृद्धि के लिए आवश्यक है।
- पारिस्थितिक संतुलन: नाइट्रोजन चक्र वातावरण, मिट्टी और जीवित प्राणियों के बीच नाइट्रोजन का संतुलन बनाए रखता है।
Conclusion | निष्कर्ष
The nitrogen cycle is a vital natural process that sustains ecosystems and supports life on Earth. It ensures the availability
of nitrogen to plants and animals, allowing for the synthesis of proteins and the growth of organisms.
नाइट्रोजन चक्र एक महत्वपूर्ण प्राकृतिक प्रक्रिया है जो पारिस्थितिक तंत्र को बनाए रखती है और पृथ्वी पर जीवन का समर्थन करती है। यह पौधों और जानवरों के लिए नाइट्रोजन की उपलब्धता सुनिश्चित करती है, जिससे प्रोटीन का संश्लेषण और जीवों की वृद्धि संभव होती है।

Leave a Reply